Hex
to binary: two solutions in Matlab
|
To convert a value from hex to binary,
we first need
to know what a hexadecimal number is.
A major numbering system
used in digital systems is the
hex
system, also known as base 16. In this system,
the numbers are
counted
from 0 to F. In base 16 we need 16 different symbols, decimal
numbers
10 through 15 are represented by letters A through F, respectively.
|
The binary system (base
2) has only two symbols, '0' and '1'.
The following table shows
the meaning of all the symbols in
the hexadecimal numbering system and their conversion to
decimal or binary equivalents.
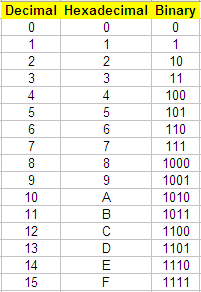
To convert a value from hex
to binary, you merely
translate each hex symbol to the equivalent 4-bit binary group. For
example,
the hex number A5A5 translates into the binary
1010010110100101 equivalent.
Solution 1. Conversion from hex to decimal, and
then from decimal to binary
In Matlab, we can go from
hexadecimal
to decimal, and then, from
decimal to
binary. We can embed one instruction into the other,
like this:
bin_str =
dec2bin(hex2dec(hex_str))
So, we
can use this concept, like this:
hex_str
= 'AF5'
bin_str =
dec2bin(hex2dec(hex_str))
Matlab’s answer is:
bin_str = 101011110101
It’s
important to remember that both binary
numbers and hexadecimal
ones are treated
as strings
in Matlab.
Solution 2. Conversion using a
Switch-Case structure
Now, let’s say that we want to
explore how the hex characters are separated to form the
binary symbols and how we can manipulate our own
strings
(binary and hexadecimal).
We can
develop a function
to translate the table shown
before. Our proposed method uses a switch-case
structure.
%
Hex to binary conversion
function b =
h2b(h)
switch h
case {'0'}
b = '0000';
case {'1'}
b = '0001';
case {'2'}
b = '0010';
case {'3'}
b = '0011';
case {'4'}
b = '0100';
case {'5'}
b = '0101';
case {'6'}
b = '0110';
case {'7'}
b = '0111';
case {'8'}
b = '1000';
case {'9'}
b = '1001';
case {'A', 'a'}
b = '1010';
case {'B', 'b'}
b = '1011';
case {'C', 'c'}
b = '1100';
case {'D', 'd'}
b = '1101';
case {'E', 'e'}
b = '1110';
case {'F', 'f'}
b = '1111';
end
Now, we have to call
the function for every hex character in the string, to convert each to
a 4-bit binary number. One possible
solution to
separate the hex characters into 4-bit groups is shown here:
hex_str
= input('Enter
hexadecimal number: ', 's');
n =
length(hex_str);
bin_str
= '';
for h = 1 :
n
bin_str
= [bin_str h2b(hex_str(h))];
end
bin_str
Let’s
try this routine.
Enter hexadecimal number:
af50
bin_str
= 1010111101010000
Enter
hexadecimal number: 15A7
bin_str
= 1010110100111
From
'Hex to binary' to home
From
'Hex to binary' to 'Matlab Programming'

|